Engineering for Health
Welcome to the Institute of Biomedical Engineering (IBT) at Karlsruhe Institute of Technology (KIT). For more than 60 years we have been active in research and teaching in the field of biomedical engineering.
In interdisciplinary projects together with medical doctors and medical industry, we investigate new technical systems that help to diagnose diseases earlier and more accurately as well as systems that make therapies more successful.
The main focus of the research program of Prof. Dr. Werner Nahm's group is optical systems in medicine and life sciences. Current projects are focussing on surgical visualization and optical diagnosis [more].
The group of PD Dr. Axel Loewe develops computational models of the heart and applies them to cardiological problems. We focus on cardiac electrophysiology and elastomechanics to contribute to answer clinical questions such as the genesis of e.g. cardiac arrhythmias and appropriate treatment strategies. Signal processing of cardiac signals (ECG and electrograms), machine learning, and artificial intelligence are further focus fields [more].
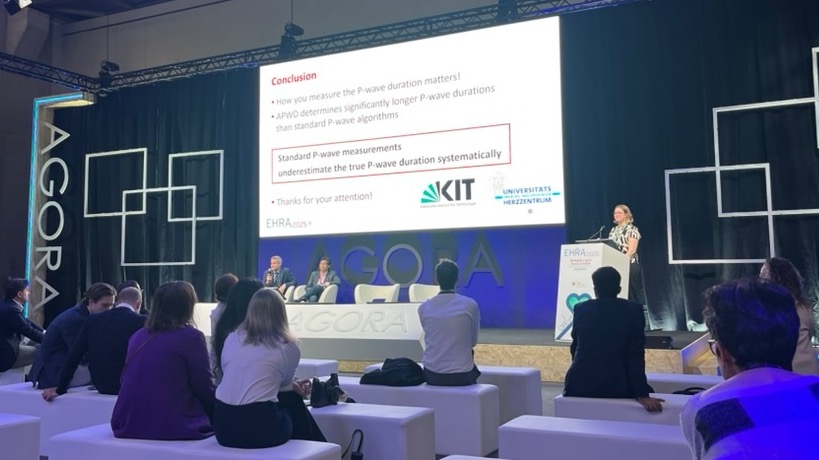

From March 30 to April 1, the annual meeting of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) took place, bringing together scientists, healthcare professionals, and key stakeholders from around the world involved in arrhythmia management. Axel Loewe and Silvia Becker represented the IBT at the event. Additionally, Silvia gave a presentation on why it matters how the P-wave is measured in the ECG.
More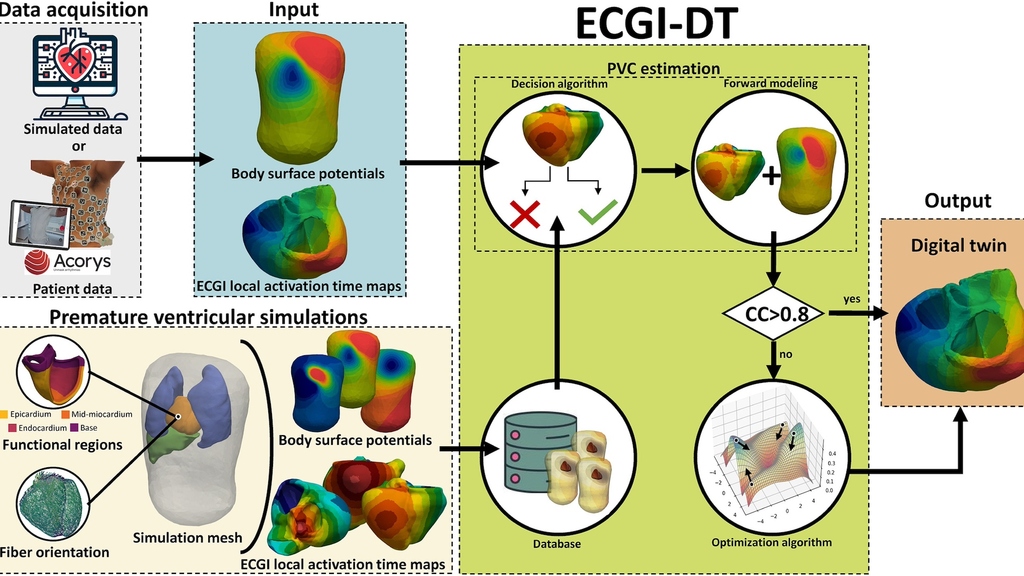
Accurately identifying the origin of premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) is crucial for improving diagnosis and treatment. Read more about this innovative approach led by a collaborative research team, including contributions from CaMo IBT.
More
From March 12 to 14, the E-Science Days took place in Heidelberg with the theme “Research Data Management: Challenges in a Changing World.” Axel Loewe and Silvia Becker represented the IBT in the workshop “Information Infrastructures in the Era of Artificial Intelligence: Opportunities and Challenges,” organized by the Leibniz ScienceCampus DiTraRe. Additionally, Silvia Becker, together with Lea Singson from FIZ Karlsruhe, gave a presentation on the legal aspects of digital twins and synthetic ECGs.
More
Numerical simulation makes it possible to model very different processes, from the weather to nuclear fusion to individual body organs. This requires highly scalable algorithms that can be put together from a mathematical library like a construction kit.
An article in the current issue of c't Magazine für Computertechnik reports on the research at KIT's Institute of Biomedical Engineering and collaborators.
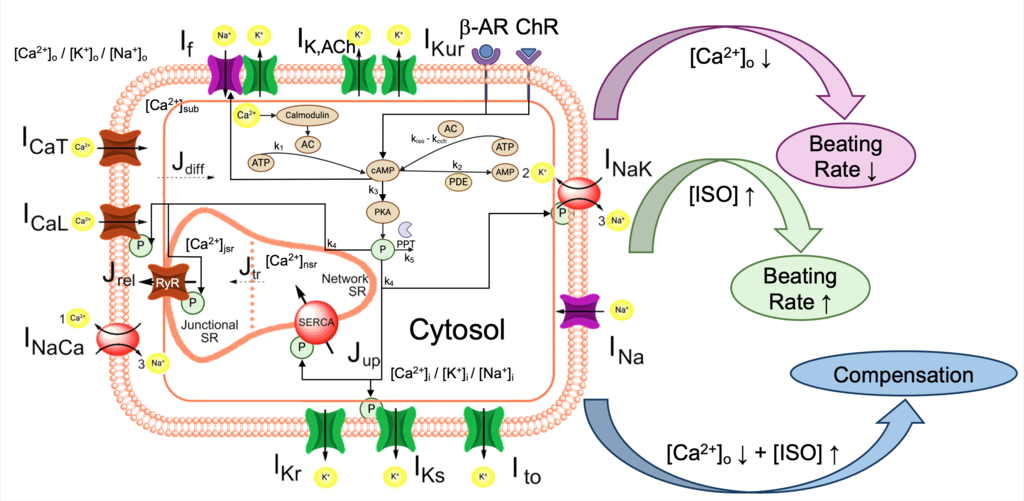
A new paper investigating the interactions between reduced extracellular calcium levels and sympathetic stimulation as a compensatory mechanism, potentially contributing to sudden cardiac death in chronic kidney disease patients, has been published in the Journal of Physiology.
More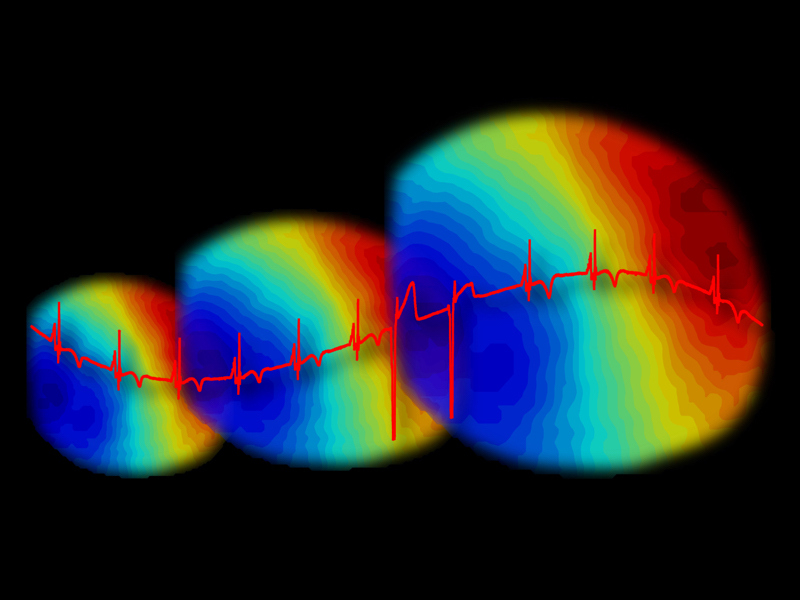
The Gordon Research Seminar and on Cardiac Arrhythmia Mechanisms was held in Barga from February 22 to 27. It covered a wide range of topics, from atrial and ventricular mechanisms to micro- and ultrastructures of individual cardiac muscle cells. Christian, Moritz, and Axel (on behalf of Tobias) presented their work.
More